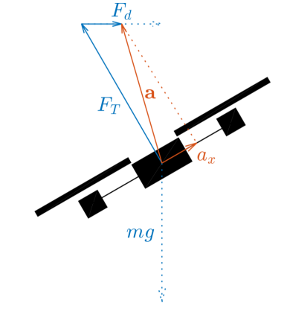
During flight, gravity, thrust and drag act on the quadrotor. Gravity is not measured by accelerometers and the thrust only acts along the drone's vertical axis. Therefore, only the drag is measured along the quadrotor's horizontal axes. Using a simple linear drag model, this deceleration can be transformed back into an estimate of the drone's airspeed.
The advantages of this method are that the acceleration is not integrated over time (the only source of drift is the drift of the sensor itself) and that no knowledge of the quadrotor's attitude or other states is required.
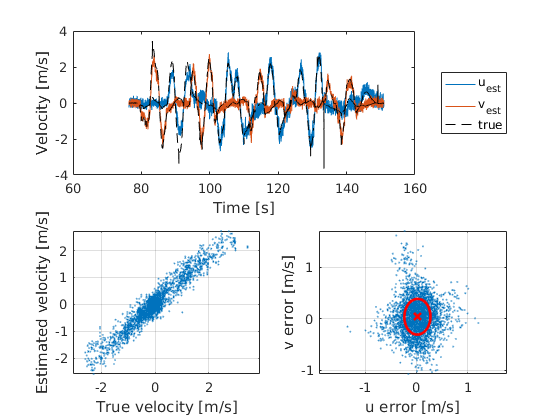
The following results were obtained from a flight test performed on an AR.Drone 2.0 inside the TU Delft Cyberzoo. The ground-truth velocities are obtained through the Optitrack system.
Add to your firmware section: This example contains all possible configuration options, not all of them are mandatory!
These initialization functions are called once on startup.
<!DOCTYPE module SYSTEM "module.dtd">
<module name="dragspeed">
<doc>
<description>
Estimate the velocity/airspeed of rotorcraft by measuring the drag force.
@image html images/airborne/modules/dragspeed/dragspeed.png
During flight, gravity, thrust and drag act on the quadrotor.
Gravity is not measured by accelerometers and the thrust only acts along
the drone's vertical axis. Therefore, only the drag is measured along the
quadrotor's horizontal axes. Using a simple linear drag model, this
deceleration can be transformed back into an estimate of the drone's
airspeed.
The advantages of this method are that the acceleration is not integrated
over time (the only source of drift is the drift of the sensor itself)
and that no knowledge of the quadrotor's attitude or other states is
required.
This module makes the following assumptions:
- The drag acting on the quadrotor grows linearly with velocity.
- The size and weight of the drone are constant (changes in size and/or
weight require re-calibration).
- Pitch and roll angles are small (less than ~20 deg).
- No wind (when used as ground speed).
Usage instructions
------------------
1. Calibrate zero (recommended before each flight)
1. For the best results, ensure that the INS velocity is as accurate as
possible (e.g. use Optitrack and set the INS type to
gps_passthrough) and set DRAGSPEED_SEND_ABI_MESSAGE to FALSE.
2. Bring the drone to a stationary hover.
3. In the GCS under settings/dragspeed, set "Calibrate Zero" to 1.
4. Keep the drone stationary until "Calibrate Zero" returns to 0.
5. (Optional) Copy the new Zero_X and Zero_Y values to the
DRAGSPEED_ZERO_X and _Y defines in the airframe file.
2. Calibrate drag coefficient (new airframes or after change in weight or
shape)
1. For the best results, ensure that the INS velocity is as accurate as
possible (e.g. use Optitrack and set the INS type to
gps_passthrough) and set DRAGSPEED_SEND_ABI_MESSAGE to FALSE.
2. Ensure the zero measurement is calibrated first. Drag coefficient
calibration will not start unless Zero_X and _Y values are
available.
3. In the GCS under settings/dragspeed, set "Calibrate Coeff" to 1.
4. Fly the drone around along the body x and y axes. The drag
coefficient is updated at speeds larger than 0.5m/s.
5. Calibration is finished when "Calibrate Coeff" returns to 0. Check
the results by comparing the estimated and INS velocities in the
DRAGSPEED telemetry message.
6. Copy the new Coeff_X and Coeff_Y values to the DRAGSPEED_COEFF_X
and _Y defines in the airframe file.
3. By default, the estimated velocity is sent through the
VELOCITY_ESTIMATE ABI message to the INS. The estimated velocity can
also be read from the dragspeed struct.
Calibration from flight plan
----------------------------
Calibration can be started from the flight plan by calling
dragspeed_calibrate_zero() or dragspeed_calibrate_coeff(). Progress of the
calibration can be monitored through dragspeed_is_calibrating(), which
returns TRUE while either calibration routine is in progress.
Example results
---------------
The following results were obtained from a flight test performed on an
AR.Drone 2.0 inside the TU Delft Cyberzoo. The ground-truth velocities
are obtained through the Optitrack system.
@image html images/airborne/modules/dragspeed/example_result.png
The following settings were used:
- DRAGSPEED_COEFF_X = 0.62
- DRAGSPEED_COEFF_Y = 0.85
- DRAGSPEED_FILTER = 0.8
</description>
<define name="DRAGSPEED_SEND_ABI_MESSAGE" description="Send VELOCITY_ESTIMATE ABI messages" value="TRUE|FALSE (default: TRUE)"/>
<define name="DRAGSPEED_ACCEL_ID" description="Accelerometer ABI ID to subscribe to (default: ABI_BROADCAST)"/>
<define name="DRAGSPEED_COEFF_X" description="Drag coefficient (mu/m) of the linear drag model along the body x axis, where m*a = v*mu"/>
<define name="DRAGSPEED_COEFF_Y" description="Drag coefficient (mu/m) of the linear drag model along the body y axis, where m*a = v*mu"/>
<define name="DRAGSPEED_ZERO_X" description="Accelerometer reading (x axis) when stationary [m/s^2]"/>
<define name="DRAGSPEED_ZERO_Y" description="Accelerometer reading (y axis) when stationary [m/s^2]"/>
<define name="DRAGSPEED_R" description="Velocity measurement noise variance [(m/s)^2]"/>
<define name="DRAGSPEED_FILTER" description="First-order low-pass filter strength [0..1] (default: 0.8)"/>
</doc>
<settings>
<dl_settings>
<dl_settings name="dragspeed">
<dl_setting shortname="Calibrate zero" var="dragspeed.calibrate_zero" min="0" step="1" max="1"/>
<dl_setting shortname="Zero_X" var="dragspeed.zero.x" min="-2.0" step="0.01" max="2.0"/>
<dl_setting shortname="Zero_Y" var="dragspeed.zero.y" min="-2.0" step="0.01" max="2.0"/>
<dl_setting shortname="Calibrate coeff" var="dragspeed.calibrate_coeff" min="0" step="1" max="1"/>
<dl_setting shortname="Coeff X" var="dragspeed.coeff.x" min="0" step="0.01" max="2.0"/>
<dl_setting shortname="Coeff Y" var="dragspeed.coeff.y" min="0" step="0.01" max="2.0"/>
<dl_setting shortname="Filter" var="dragspeed.filter" min="0" step="0.01" max="1.0"/>
</dl_settings>
</dl_settings>
</settings>
<header>
<file name="dragspeed.h"/>
</header>
<init fun="dragspeed_init()"/>
<makefile>
<file name="dragspeed.c"/>
</makefile>
</module>